ERC 7231
The ERC 7231: Identity Aggregated NFT, pushes the boundaries of solving identity problems with Identity Aggregated NFT, i.e., the individual-authenticated aggregation of web2 and web3 identities to NFTs (SBTs included).
This standard extends ERC-721 by binding individuals’ Web2 and Web3 identities to non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and soulbound tokens (SBTs). By binding multiple identities, aggregated and compossible identity information can be verified, resulting in more beneficial onchain scenarios for individuals, such as self-authentication, social overlapping, commercial value generation from user targeting, etc. By adding a custom schema in the metadata and updating and verifying the schema hash in the contract, the binding of NFT and identity information is completed.
Designing the proposal, we considered the following problems that are solved by this standard:
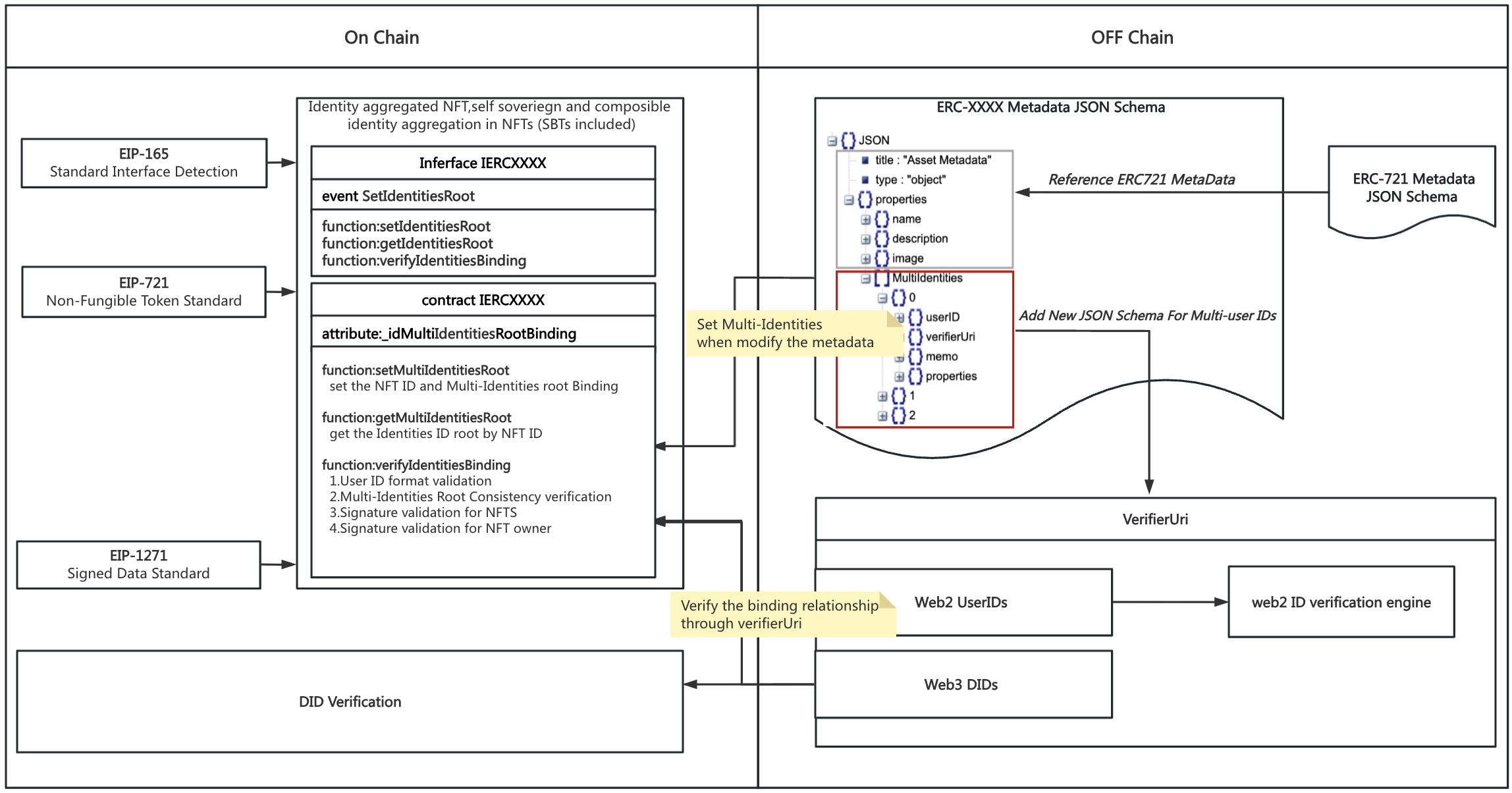
Resolve the issue of multiple ID bindings for web2 and web3. By incorporating the MultiIdentities schema into the metadata file, an authorized bond is established between user identity information and NFTs. This schema encompasses a userID field that can be sourced from a variety of web2 platforms, or a decentralized identity (DID) created on blockchain. By binding the NFT ID with the UserIDInfo array, it becomes possible to aggregate multiple identities seamlessly.
Users have full ownership and control of their data. Once the user has set the metadata; they can utilize the setIdentitiesRoot function to establish a secure binding between hashed userIDs objects and NFT ID. As only the user holds the authority to carry out this binding, it can be assured that the data belongs solely to the user.
Verify the binding relationship between data on-chain and off-chain data through signature based on ERC-1271 Through the signature method based on the ERC-1271 protocol, the verifyIdentiesBinding function of this EIP realizes the binding of the userID and NFT owner address between the on-chain and off-chain.
NFT ownership validation
UserID format validation
IdentitiesRoot Consistency verification
Signature validation from NFT owner
As for how to verify the authenticity of the individuals’ identities, wallets, and accounts, there are various methods, such as ZK-based DID authentication on-chain, and off-chain authentication algorithms, such as auth2, openID2, etc.
To learn more about this Ethereum Improvement Proposal #7231, please read here.
Last updated